Learn more about fertility nutrition
Overall wellness, including a balanced diet, has shown to positively impact reproductive health and, in some cases, enhance fertility treatment.
Dr. Dan Gehlbach concurs with colleagues in reproductive endocrinology that dietary choices can increase the chances for getting pregnant in certain women diagnosed with ovulatory dysfunction, including polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), and men presenting with sperm disorders.
The Difference Between a Fertility Diet and Nutrition
for Fertility
A balanced diet of whole-foods lowers risks for certain types of cancer, heart disease, diabetes and high blood pressure. Poor dietary habits can exacerbate infertility, but Dr. Gehlbach considers a multitude of causes of infertility before recommending a targeted fertility treatment plan.
Midwest Reproductive Center does not recommend power foods, or a fertility diet.
Nutrition for fertility involves a sensible weight loss and dietary plan to help the endocrine system function at peak performance.
Understanding the Science Behind Fertility and Nutrition
Your body’s endocrine system of glands produces hormones that regulate growth, metabolism and reproduction.
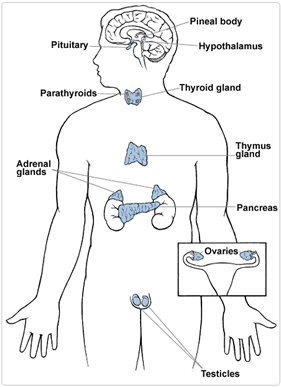
American Medical Association Diagram of the Endocrine System
Dr. Gehlbach will order blood tests to determine dysfunction with the endocrine system. Metabolic syndrome—with its two risk factors insulin resistance and central obesity—can lead to heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes and infertility.
Research Findings that Link Nutrition and Fertility
The American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM) recently presented four studies that supported a link between nutrition and fertility.
Two of the studies related to male infertility. One study linked dairy, particularly higher-fat dairy, with decreased sperm quality; the other examined carbohydrate intake. Men ages 18 to 22 showed a decline in sperm count when they consumed higher amounts of carbohydrates, which increase glycemic rates.
Findings relating to women concluded that a diet high in protein and lower in carbohydrates led to higher pregnancy rates.
Midwest Reproductive Center Conclusions on Nutrition for Fertility
- Folic acid, in addition to combating neural tube defects in utero, has been shown to increase the chances for getting pregnant.
- Overweight and underweight women may experience an interruption in regular ovulation.
- Weight loss is a powerful strategy for improving fertility and preventing diabetes.
The Midwest Reproductive Center team recognizes that the challenges you face can feel overwhelming. Fertility treatment takes physical and emotional stamina, so we provide as many patient resources as possible to support you. Contact us for a consultation with Dr. Gehlbach.



